
views
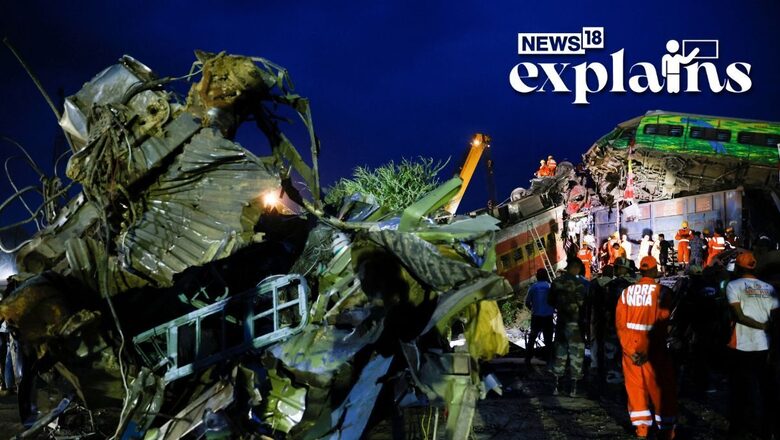
A team of the Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) on Tuesday initiated an investigation into the Odisha train accident that killed over 270 people and injured 1,100.
The CRS deals with matters pertaining to safety of rail travel and train operations. This body is not just for investigation, but also conducts inspection and issues advisories.
Here’s all you need to know about it:
VIDEO | “The Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) team is gathering information. The CBI team is also investigating, gathering information, and collecting data. Both the investigations are running parallelly," says Aditya Kumar Chaudhary, CPRO, South Eastern Railway on… pic.twitter.com/YUHPSgkTZS— Press Trust of India (@PTI_News) June 6, 2023
IN EXISTENCE SINCE BRITISH ERA
While there were different names and designations, the CRS has been in existence since the British era. Then, the construction and operation of railways was with private players and the British government of India used to appoint consulting engineers to exercise effective control over them.
Later, when the government took over the construction of Railways, the consulting engineers were designated as Government Inspectors. In 1883, their position was statutorily recognized. Then, the Inspectorate office was under the Railway Board, which was the safety controlling authority.
1939 saw the tragic Bihta derailment in Bihar. In the backdrop, the Pacific Locomotive Committee was set up, which recommended that the Railway Inspectorate should be separated from the Railway Board.
The reason was simple — those responsible for inspection of Railways should be independent of the authority administering the Railways. These recommendations were approved and in May 1941, the Railway Inspectorate was separated from the Railway Board.
Over the years, the posts underwent several name changes and the Inspectorate office was placed under the Department of Communication. It is now under the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA).
THE DESIGNATIONS & RESPONSIBILITIES
- From 1979, the designations have been the Chief Commissioner of Railway Safety (CCRS) and Commissioner of Railway Safety.
- While these Commissioners of Railway Safety are recruited from among officers of Indian Railways, they do not report to Railways. They are absorbed in the Commission of Railway Safety under the MoCA.
- Rail safety commissioners are responsible for matters related to inspecting new railways with a view to determine whether they are fit to be opened for public carriage of passengers.
- They also take up periodic inspections of any railway or rolling stock used. In case of an accident, they make inquiry into the cause.
- “They have three major roles: inspections, advisories and investigations. For every new line that is made public, the safety commissioners are the first to travel on it. Until they approve, no new lines can operate," a Ministry official told News18.
##Exclusive| Odisha Train Accident: Railway minister Ashwini Vaishnaw briefs PM Modi as he visits the #BalasoreTrainAccident site to review the situation CNN-News18's @KamalikaSengupt with more details #PMModi #OdishaTrainAccident #OdishaTrainTragedy | @akankshaswarups pic.twitter.com/QYHK7qb4sk
— News18 (@CNNnews18) June 3, 2023
MISHAP INVESTIGATIONS
As soon as the CRS receives an intimation about a serious accident, they proceed to the site. They conduct inspection of the accident site and record all particulars relevant to the accident.
They then fix a date for the inquiry, which is given publicity in the media. Officers of the local magistracy and police are separately advised of the dates of the inquiry.
The official explained that the safety commissioner takes into consideration a number of factors, including what the public has seen. “They take into account every aspect of the incident, including what the eyewitnesses have to say," the official said.
The public are invited to give evidence in the inquiry in person or to write to the Commissioner.

















Comments
0 comment