
views
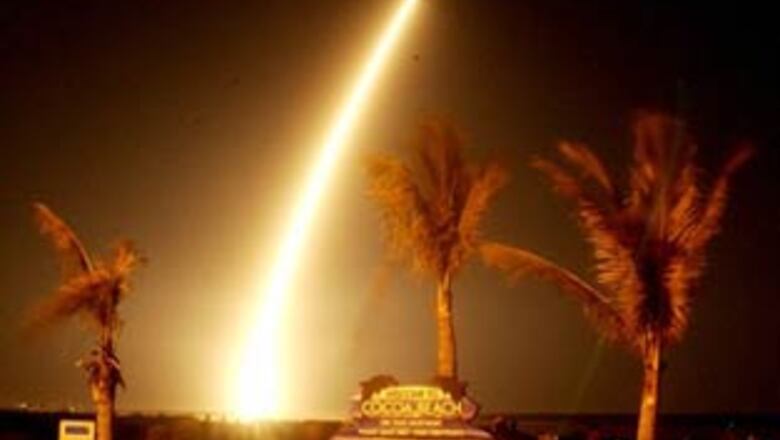
Cape Canaveral (Florida): NASA's planet-hunting spacecraft, Kepler, rocketed into space on Friday night on a historic voyage to track down other Earths in a faraway patch of the Milky Way galaxy.
It's the first mission capable of answering the age-old question: Are other worlds like ours out there?
Kepler, named after the German 17th century astrophysicist, set off on its unprecedented mission at 10:49 p.m. EST (1549 GMT), thundering into a clear sky embellished by a waxing moon.
Its mission will last at least for three-and-a-half-year and cost $600 million.
The goal is to find, if they're there, Earth-like planets circling stars in the so-called habitable zone — orbits where liquid water could be present on the surface of the planets. That would mean there are lots of places out there for life to evolve, said Kepler's principal scientist, Bill Borucki.
On the other hand, "if we don't find any, it really means Earths are very rare, we might be the only extant life and, in fact, that will be the end of Star Trek."
Once it's settled into an Earth-trailing orbit around the sun, Kepler will stare nonstop at 100,000 stars near the Cygnus and Lyra constellations, between 600 and 3,000 light years away. The telescope will watch for any dimming, or winks, in the stellar brightness that might be caused by orbiting planets.
Astronomers already have found more than 300 planets orbiting other stars, but they're largely inhospitable gas giants like Jupiter. Kepler will be looking for smaller rocky planets akin to Earth.
Kepler is designed to find hundreds of Earth-like planets if they're common and, perhaps, dozens of them in the habitable zone, Boruki said. The telescope is so powerful that from space, NASA maintains, it could detect someone in a small town turning off a porch light at night.
It won't be looking for signs of life, though. That's for future spacecraft.
NASA was counting on a successful launch to offset the loss one-and-a-half-week earlier of the space agency's Orbiting Carbon Observatory. That environmental satellite ended up crashing into the Antarctic because of rocket failure. It was a different type of rocket than the one used for Kepler.

















Comments
0 comment