views
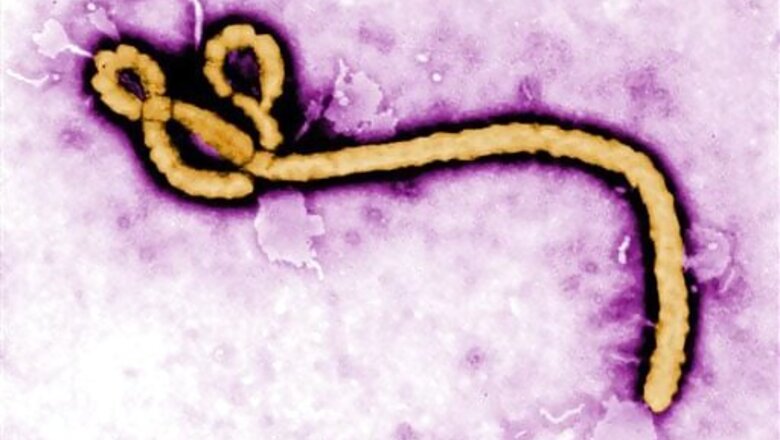
Washington: Researchers have discovered a human protein that helps fight the Ebola virus, and could one day lead to an effective therapy against the deadly disease.The newly discovered ability of the human protein RBBP6 to interfere with Ebola virus replication suggests new ways to fight the infection, according to the study published in the journal Cell. "As viruses develop and evolve proteins to bypass the body's immune defences, human cells in turn develop defence mechanisms against those viruses -- an evolutionary arms race that has been ongoing for millions of years.
"This particular defence mechanism has therapeutic potential," said Judd Hultquist, an assistant professor at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in the US."One of the scariest parts about the 2014 Ebola outbreak was that we had no treatments on hand; tens of thousands of people became sick and thousands of people died because we lacked a suitable treatment."
The US researchers are now working to create a small molecule drug that mimics the human protein and could be used in response to an Ebola virus outbreak. "A small molecule drug is the ultimate goal because these are able to enter cells more easily and, therefore, be more effective," say the researchers.The Ebola virus, like other viruses, invades host cells and uses them to replicate, usurping cellular processes to build viral proteins, which eventually become new copies of the virus.
Ever since it first broke out in 1976 the virus has claimed many live. The outbreak in 2014-2016 in regions of West and Central Africa was particularly lethal as it led to the deaths of tens of thousands of people in countries like Sierra Leone and Guinea.
Hultquist and his collaborators used mass spectrometry, a technique that identifies specific elements in a sample by mass, to search for interactions between human proteins and Ebola virus proteins. They found strong evidence for an interaction between the Ebola virus protein VP30 and the human protein RBBP6.
Further structural and computational analysis narrowed the interaction down to a small, 23-amino acid-long peptide chain."If you take that peptide and put it into human cells, you can block Ebola virus infection. Conversely, when you remove the RBBP6 protein from human cells, Ebola virus replicates much faster," Hultquist said.

















Comments
0 comment