
views
Home loan interest rates in India are the interest rates charged by banks and other financial institutions on home loans. It is important for prospective homebuyers to compare and analyse different home loan rates offered by various lenders to find the most favourable terms that suit their financial situation. Lower interest rates can lead to reduced Equated Monthly Instalment (EMI) payments and overall cost savings over the loan tenure.
The interest rate is a percentage of the loan amount that the borrower must pay to the lender in addition to the principal amount. The interest rate is usually expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR). These rates determine the cost of borrowing and influence the monthly EMI that borrowers need to pay.
Also Read: Struggling To Repay Loan? Here’s How You Can Pay On Time And Avoid Default
Home loan interest rates vary from lender to lender and from time to time. It is important to check around and compare interest rates from different lenders before you apply for a home loan. You should also consider the other terms and conditions of the loan, such as the loan amount, the repayment period, and the processing fees.
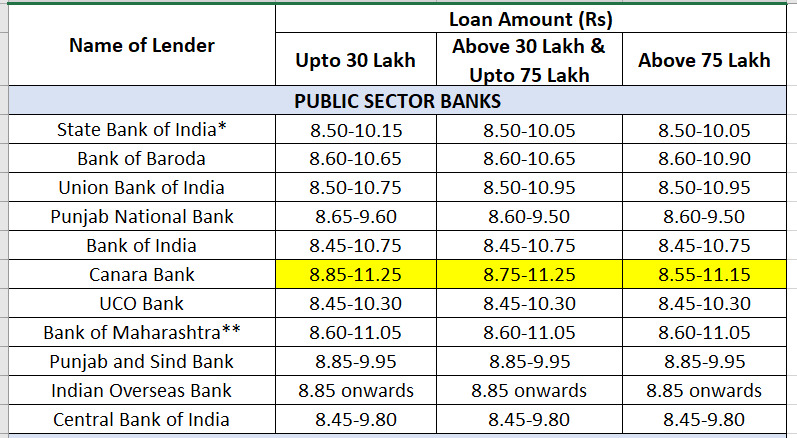
Here are two tables showing interest rates on home loans as of June 14.
Home loan interest rates: Public sector banks
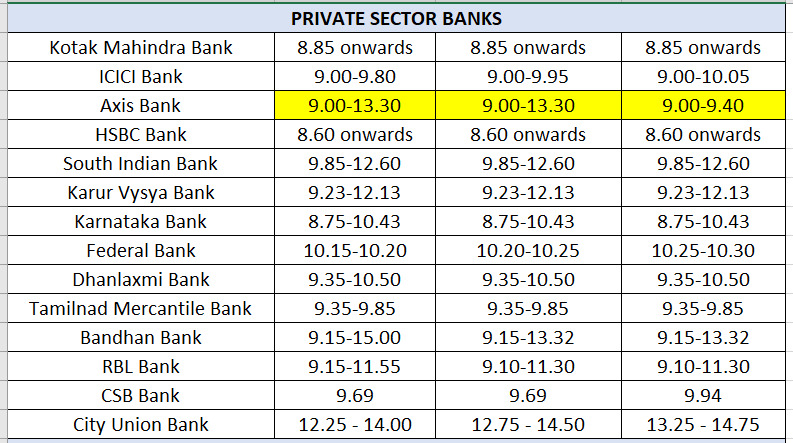
Home loan interest rates: Private sector banks
Factors influencing home loan rates
The home loan interest rate is influenced by a number of factors, including the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) repo rate, the lender’s risk assessment of the borrower, and the type of loan. The RBI’s repo rate is the rate at which banks borrow money from the RBI. When the RBI increases the repo rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money, which leads to higher home loan interest rates.
RBI in its latest MPC decision again hit the pause button and decided to keep the key benchmark policy rate (repo rate) at 6.5%.
The lender’s risk assessment of the borrower is also a factor in determining the home loan interest rate. Borrowers with good credit scores and a proven track record of repaying debt are typically offered lower interest rates than borrowers with poor credit scores or a history of late payments.
The type of loan also affects the home loan interest rate. For example, floating rate loans have interest rates that are linked to a benchmark rate, such as the RBI’s repo rate. When the benchmark rate changes, the interest rate on the floating rate loan will also change.
Fixed rate loans have interest rates that are fixed for a period of time, such as five years. This means that the interest rate on the fixed rate loan will not change during the fixed rate period.

















Comments
0 comment