
views
There are some specialty first aid equipment that can stimulate coagulation to help reduce blood loss after a serious injury. On another note, if your blood is not clotting enough to quickly stop bleeding after minor injuries, speak with your doctor as soon as possible.[1]
X
Research source
Speeding Up Coagulation With Kaolin and Zeolite

Seek medical assistance for a serious wound. Injuries from accidents, violence, or animal bites, as well as dirty wounds with foreign objects, require quick first aid and professional medical attention. This is partly because coagulation is insufficient to prevent bleeding from hemorrhaging and other major injuries, even if you have healthy blood. If you are able to see muscle or fat tissue or unable to press the edges of the wound together using gentle pressure, get to a hospital. Other reasons a wound should be considered serious include close proximity to a joint or genitalia, a jagged pattern of broken skin, a continuous or pulsing flow of blood, or impalement by something visibly unclean. Reduce bleeding for transport of an injured person by applying pressure bandages and, if necessary, a tourniquet.
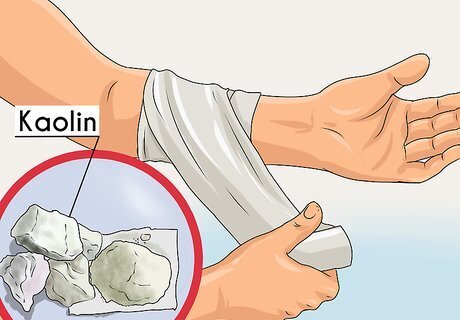
Use kaolin dressing to stimulate clotting. Kaolin is a mineral that has been used to help reduce blood loss following major injuries, including those sustained in combat. Use dressing that is impregnated with kaolin to apply a pressure bandage to the wound. The pressure counteracts the blood pressure that would otherwise push blood out of the body, while the kaolin will prompt the coagulation process to begin. Get kaolin-treated dressings for your vehicle’s first aid kit, or to carry in first aid kits while spending time in remote areas. They can be found a specialty supplies stores and online.
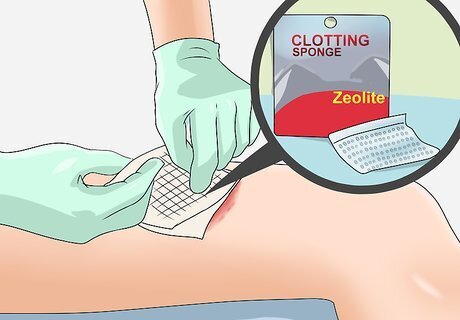
Plug major wounds with zeolite bags. Another first aid item used to treat injuries that involve major hemorrhaging are small mesh bags that contain the mineral zeolite. When activated, these bags not only fill a large wound and apply even pressure throughout, the zeolite prompts the blood in the area to begin coagulating and can even speed up the process. Mesh pouches filled with zeolite can be purchased from specialty first aid retailers. They will be easier to find online than in stores. These items are designed to help treat large wounds, and are designed to stabilize wound victims for transport to a medical facility. QuikClot is a zeolite containing product that stops bleeding fast.
Diagnosing a Bleeding Disorder
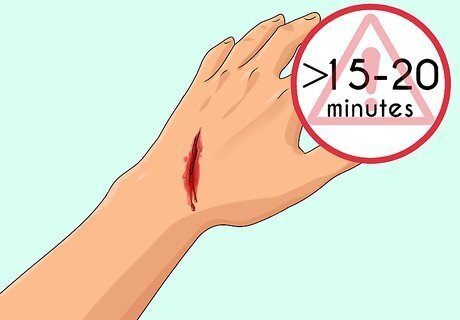
Monitor the length of time that a minor cut bleeds. The most telling sign that your blood is not coagulating fast enough is excessive bleeding. It should not take longer than ten minutes for a small cut or scrape to stop bleeding, with anywhere from one to nine minutes being normal. If you are still bleeding after ten minutes, see a doctor as soon as possible. If you or someone else is losing substantial amounts of blood, provide first aid and get to a hospital as quickly as possible.
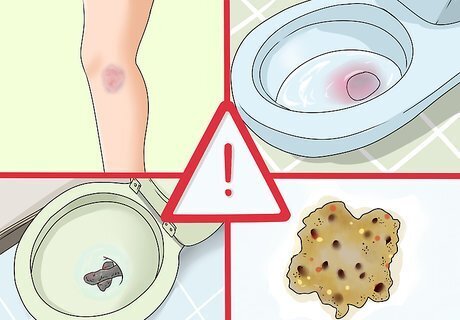
Recognize other symptoms of a potential bleeding disorder. In addition to excessive bleeding following a minor injuries, other symptoms may also indicate a bleeding disorder. These include unexpected or sudden bruising, red or pink urine, and black or bloody bowel movements. Dark spots in your vomit (which will look like coffee grounds) may also indicate a bleeding disorder. If any of these symptoms appear, see a doctor as soon as possible. Recurring or persistent dizziness, headaches, and vision changes may also indicate a bleeding disorder, as well as joint pain, bleeding gums, or irregularly heavy or long-lasting menstrual periods.
Get a formal medical diagnosis. Your doctor will need to do blood tests to determine whether you have a bleeding disorder. In addition to evaluating the contents of your blood (such as the amount of platelets and proteins), your doctor will also order a test to determine the efficiency of your blood’s coagulation process.
Consider treatment options. There may be a serious underlying cause for a bleeding disorder that requires treatment. There are also treatments that can help remedy symptoms of a bleeding disorder directly. Follow your doctor’s guidance regarding any sort of treatment for a bleeding disorder. Potential treatment options include Vitamin K injections, plasma or platelet transfusions, or medications. If you are diagnosed with a bleeding disorder, expect to take medication to help ensure your blood will be able to coagulate when necessary.
Considering Related Factors

Drink less alcohol. Alcohol reduces the “stickiness” of the platelets in your blood, making them less capable of clumping together to form a blood clot. In fact, the claim that alcohol in moderation is “good for you” stems from this effect. However, if you have a condition that causes your blood to coagulate slowly, drinking alcohol can worsen this symptom. While one or two alcoholic beverages from time to time are unlikely to have an affect on your blood’s ability to coagulate, frequent or heaving drinking can put you at greater risk.
Ask your doctor about aspirin and NSAID use. Aspirin is commonly recommended as a way to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke, but it can also thin your blood, making it harder for it to clot. NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen. These are available over-the-counter and often used for pain relief. If you notice that your blood doesn’t clot well or that you bruise easily after you start taking aspirin or NSAIDs, talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of continuing to take these drugs. If your doctor has recommended taking aspirin, don’t stop taking it without discussing it with your doctor.
Avoid supplements and food that can thin your blood. Common dietary supplements such as fish oil, Coenzyme Q10, and vitamin E thin your blood and make it harder for it to coagulate. Consult with your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking blood thinning medications. Additionally, foods can have the same effect, including raisins, prunes, cherries, cranberries, blueberries, grapes, strawberries, tangerines, oranges, onions, olive oil, garlic, ginger, green tea, papaya, and pumpkin seeds. Common herbs that can thin your blood include cinnamon, curry, cayenne pepper, paprika, thyme, turmeric, oregano, and peppermint. Alternatively, some foods can decrease bleeding, such as green leafy vegetables, broccoli, celery, and carrots. Eating pineapple a few days before surgery can reduce bleeding and bruising post-operation.
Talk to your doctor about the risk of blood clots. For some people, the risk of blood clots is more dangerous than potential blood loss caused by slow coagulation. In fact, the clots that save your body from losing blood when you are injured can be deadly when they form within an artery or vein. In part for this reason, you should never take steps to help your blood coagulate and clot without professional medical guidance.

Consult a physician in an emergency. If you are experiencing dangerous blood loss, there are some medications that are used exclusively for emergency treatment. For instance, antifibrinolytic drugs prevent blood clots from breaking down and can help prevent blood loss during surgery or following a serious injury. If you have an emergency situation, don’t hesitate to get medical attention because there are medicines available that can help your blood clot better. These drugs are administered by medical professionals, so seek treatment immediately.

















Comments
0 comment