
views
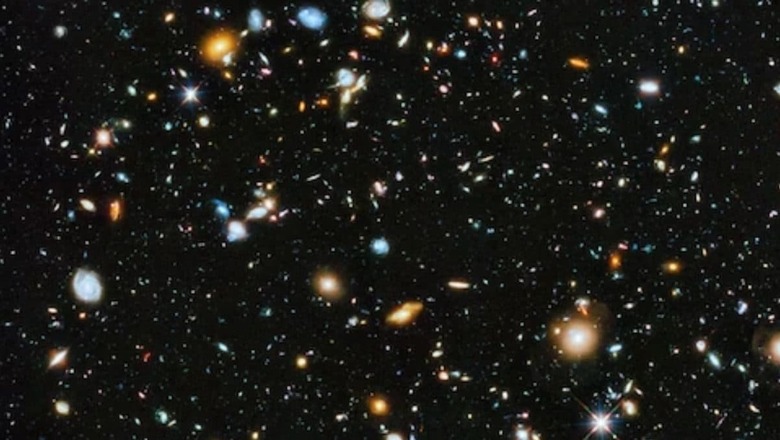
One of the most intriguing things about our universe is that it is terrifying and mysterious, and equally beautiful at the same time with so many celestial bodies. However, our scientists relentlessly work to discover more about it like how they have successfully calculated the maximum possible hottest temperature in the universe.
The coldest possible temperature is simple to measure since the coolest thing can be at absolute zero degrees Kelvin. If converted into another unit, it becomes -273.15 degrees Celsius and -459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. Interestingly, scientists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology were able to reach closer to this temperature only recently. But have you ever wondered if is there an “absolute hot” or can something can reach such levels of temperature? Unsurprisingly, it is not simple, because how can anyone even measure a maximum temperature?
Maximum temperature means the highest level of activity a particle can engage in, as the friction between the particles causes heat. So, in theory, the highest possible temperature is calculated to be 142 nonillion kelvins, which means that you have to attach thirty-two zeroes after it and it can only be reached if the particles attain a state called the thermal equilibrium. As per the standard particle physics, this is believed to be the highest level of temperature, known as the Planck temperature.
Scientists believe nothing can be close to this temperature in the current universe, although it could have existed at the very beginning of everything, but just for a brief moment. That time is believed to be the only period in the history of the universe where the temperatures reached close to the Planck temperature. To compare, the highest temperature that has been observed was in a Large Hadron Collider. While smashing the particles of gold, the temperature recorded for a split second was 7.2 trillion degrees Fahrenheit.



















Comments
0 comment