
views
Using the Settings Menu from Within Windows

Move your mouse or index finger to the right edge of the screen. This displays the charms menu to the right. You can use this option if you are still able to log in to Windows.

Click Settings Windows Settings. It's the icon that resembles a gear in the charms menu to the right.
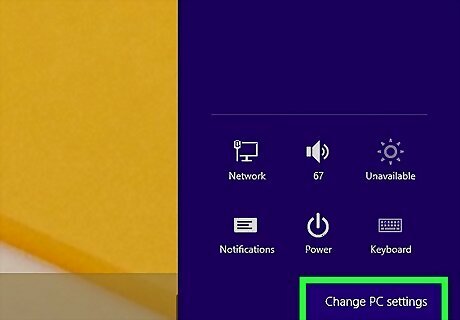
Click Change PC Settings. It's at the bottom of the Settings menu on the right.
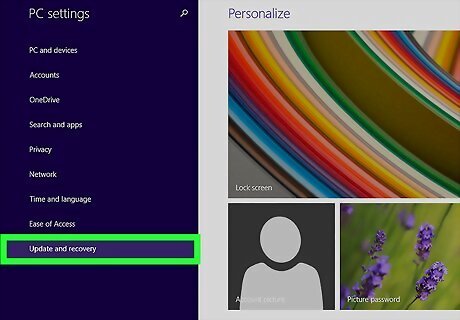
Click Update and recovery. It's at the bottom of the Settings menu on the left.
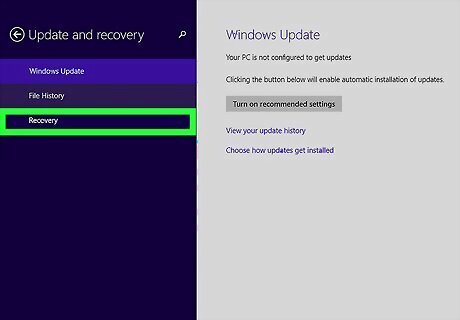
Click Recovery. It's the last option in the "Update and recovery" menu.
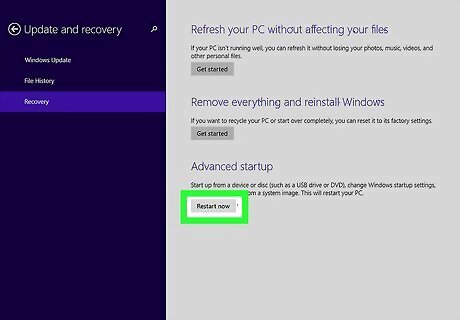
Click Restart Now. It's the last option below "Advanced startup". This opens the advanced restart menu.
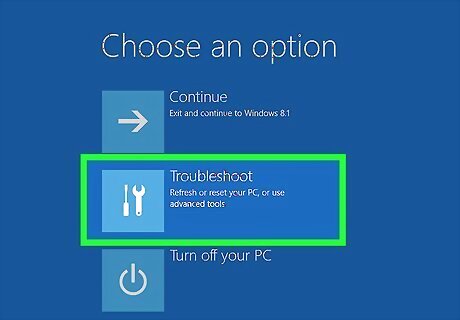
Click Troubleshoot. It's the second option. It's next to an icon that resembles tools. This opens the "Troubleshoot" menu.
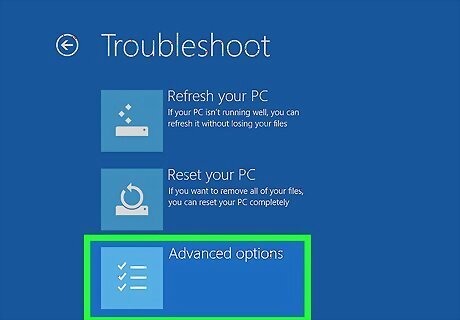
Click Advanced options. It's the last option in the "Troubleshoot" menu. It's next to an icon that resembles a checklist.

Click Startup Settings. It's the last option in the "Advanced options" menu. It's next to an icon that resembles a gear.
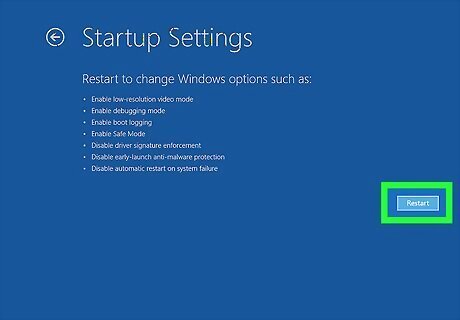
Click Restart. It's in the lower-right corner.
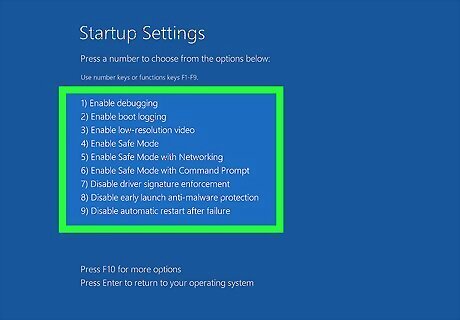
Press the key that corresponds to one of the safe mode options. There are 3 safe mode options in the menu. They are as follows: Press 4 or F4 to enter safe mode with minimal drivers and services. Press 5 or F5 to enter safe mode with internet access. Press 6 or F6 to enter the command prompt with no graphical user interface (advanced users only).
Using System Configuration From Within Windows
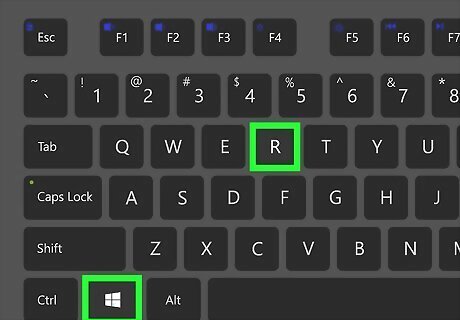
Press ⊞ Win+R. This opens the "Run" utility. Alternatively, you can right-click the Windows Start menu and click Run.
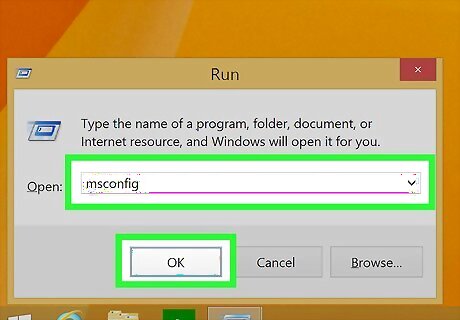
Type msconfig and click Ok. Enter "msconfig" in the text field next to "Open." Then click Ok. This opens the System Configuration utility.
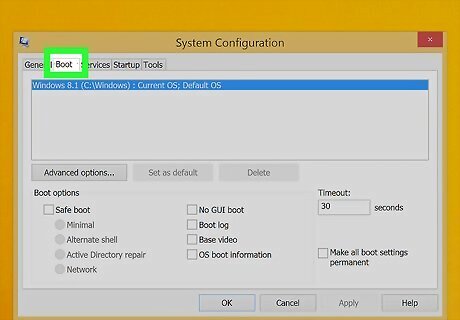
Select the Boot tab. It's the second tab at the top of the System Configuration window.
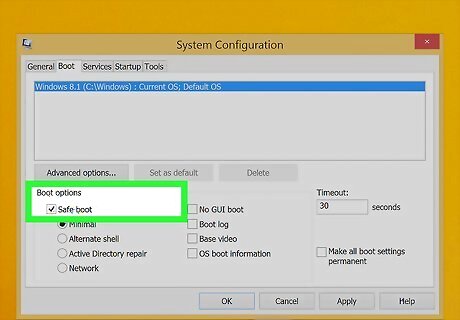
Check Windows Checked '“Safe Boot." It's the first option below "Boot."
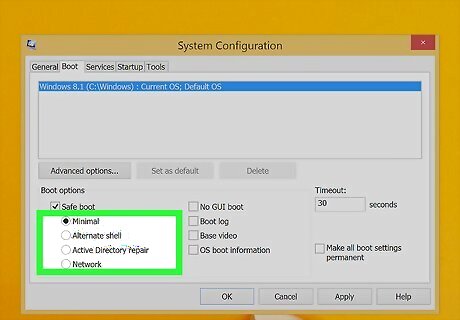
Select a boot option. Click the radio button next to the boot option you want. Your options are as follows: Minimal: This boots Windows in safe mode with the standard Windows graphical user interface (GUI), but with minimal drivers and services. You can use this option to fix most problems. Active Directory Repair: This starts Windows in safe mode with access to hardware information. Use this option if you need to repair corrupt files in the Active Directory. Network: This starts Windows in safe mode with network drivers enabled. This allows you to connect to the internet while in safe mode. Alternate Shell: This option boots Windows into a command prompt interface with no graphical user interface. This option is for advanced users only.
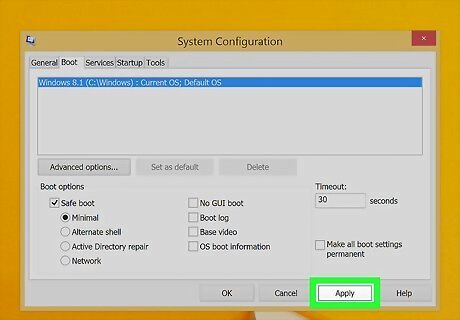
Click Apply followed by Ok. This applies the safe mode boot settings. You will be asked if you want to restart your computer.
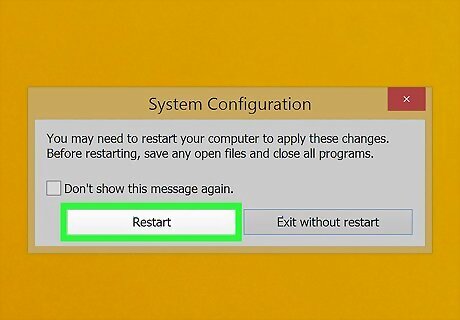
Click Restart. It's in the pop-up that appears when you click Ok. Your computer will boot into safe mode. Windows will keep booting into Safe Mode until you disable it. To disable Safe Mode, repeat these steps to open the System Configuration utility, click the Boot tab, and uncheck the "Safe Mode" option. Click Apply and reboot your computer.
From the Windows Sign In Screen
Power on your computer. Press the power button on your laptop or computer tower to boot up your computer. Do not sign in to Windows on the sign-in screen.
Click the power icon Windows Power. It's the icon that resembles a circle with a line going through the top. This displays the Power menu.
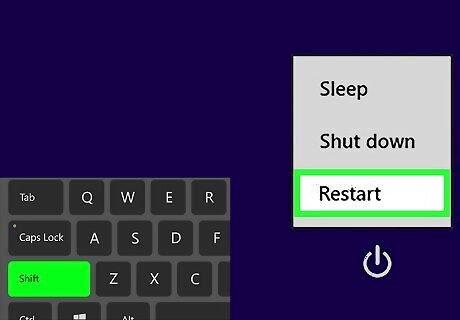
Hold ⇧ Shift and click Restart. This displays a menu with advanced restart options.
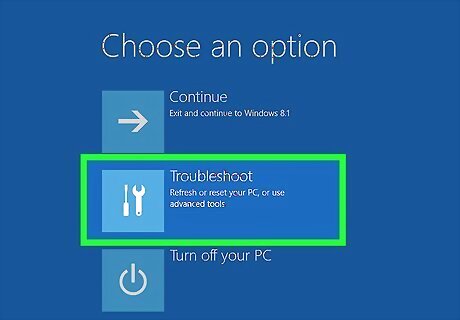
Click Troubleshoot. It's the second option. It's next to an icon that resembles tools. This opens the "Troubleshoot" menu.
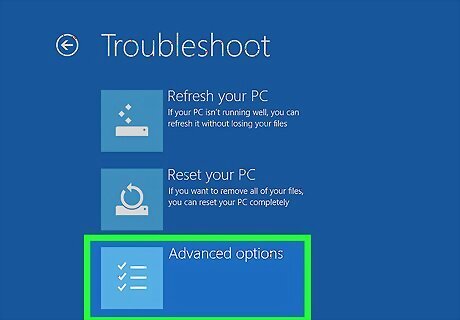
Click Advanced options. It's the last option in the "Troubleshoot" menu. It's next to an icon that resembles a checklist.

Click Startup Settings. It's the last option in the "Advanced options" menu. It's next to an icon that resembles a gear.
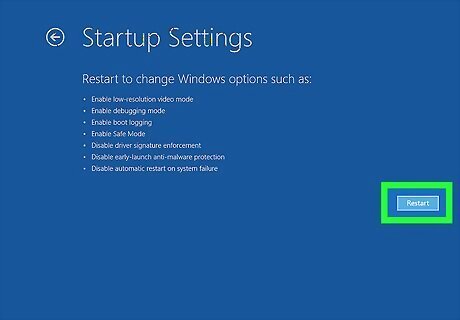
Click Restart. It's in the lower-right corner.
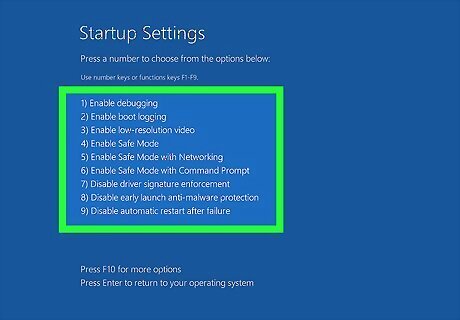
Press the key that corresponds to one of the safe mode options. There are 3 safe mode options in the menu. They are as follows: Press 4 or F4 to enter safe mode with minimal drivers and services. Press 5 or F5 to enter safe mode with internet access. Press 6 or F6 to enter the command prompt with no graphical user interface (advanced users only).
Interrupting The Boot Process
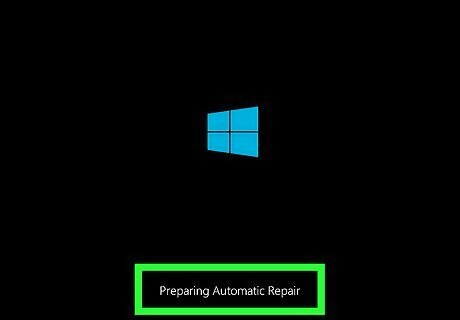
interrupt the boot process three times. If you are unable to boot into the Windows sign-in screen, you can force windows to enter a repair mode by interrupting the boot process three times. To do so, press the power button to boot up your computer. Then press and hold the power button while your computer boots up. Hold it until it powers off. Repeat three times.
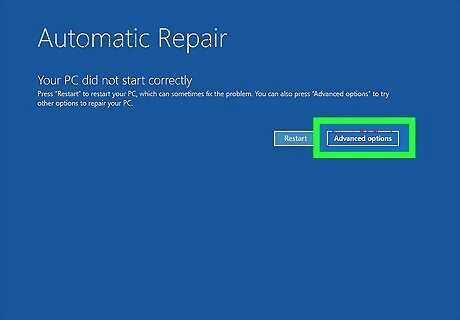
Click Advanced Options. When the "Automatic Repair" screen appears, click Advanced Options in the lower-right corner.

Click Startup Settings. It's the last option in the "Advanced options" menu. It's next to an icon that resembles a gear.
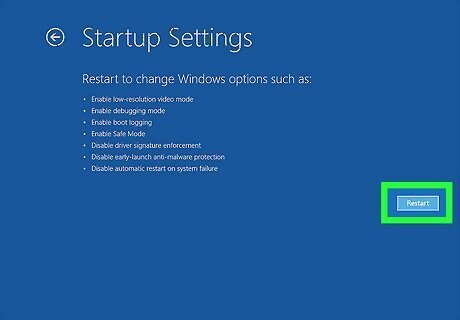
Click Restart. It's in the lower-right corner.
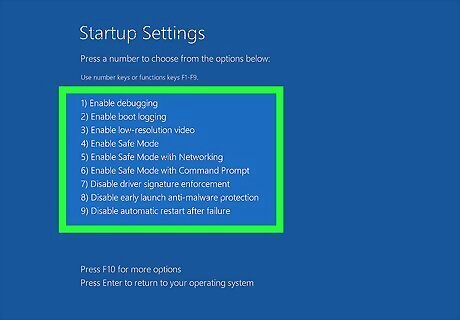
Press the key that corresponds to one of the safe mode options. There are 3 safe mode options in the menu. They are as follows: Press 4 or F4 to enter safe mode with minimal drivers and services. Press 5 or F5 to enter safe mode with internet access. Press 6 or F6 to enter the command prompt with no graphical user interface (advanced users only).
















Comments
0 comment