
views
Losing Water Weight

Drink more water to flush out extra fluids. It may seem counter-intuitive, but the more water you drink, the less you’ll retain. Drink water or other hydrating fluids, such as light fruit juices or low-sodium broths, to keep excess fluids moving through your system. You can also boost your fluid intake by eating plenty of water-rich foods, like juicy fruits and vegetables. Avoid sports drinks, which contain sodium and sweeteners that can cause you to retain fluids. Steer clear of dehydrating beverages, like alcohol, tea, and coffee. If quitting alcohol, even temporarily, is difficult for you, talk to your doctor. They can offer advice on how to quit or cut back. Drinking coffee can also be a hard habit to shake. Consider weaning yourself off slowly for a few days before you drop it altogether.

Cut back on salt to reduce water retention. When you eat a lot of salt, it encourages your body to retain fluids. Avoid foods that are high in salt, such as processed meats, salty chips and crackers, and sports drinks. When you’re cooking or eating a meal, resist the urge to add a bunch of salt. Eating foods high in potassium, such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and tomatoes, can help your body keep your body’s fluids at a normal level. Experiment with alternatives to salt when you’re cooking, such as black pepper, garlic powder, or flavorful vegetable oils (like sesame oil). You can avoid excess salt by cooking your own foods from fresh, unprocessed ingredients.

Steer clear of carbs to lose water weight quickly. Eating lots of carbohydrate-rich foods can cause you to retain water. For this reason, many people lose a lot of water weight quickly when they first switch to a low-carb diet. Try cutting out foods such as white bread, pasta, potatoes, and baked sweets. Replace high-carb foods with fruits and vegetables that are high in fiber, like berries, leafy greens, and legumes (beans and peas). Cutting carbs out of your diet is good for short-term weight loss, but it’s not a good long-term solution. To maintain a healthy diet, eat sources of complex carbs such as whole-grain breads and pastas, brown rice, and beans.

Exercise to break a sweat. When you exercise, you lose excess water and salt through perspiration. Try running, hiking, or going for a brisk walk to get your blood pumping and work up a good sweat. Try circuit training or other high-intensity workouts to lose fluids quickly. Don’t forget to drink plenty of water while you exercise. If you get dehydrated, you’ll only retain more water!

Ask your doctor about diuretic medications. Certain health conditions can cause you to retain a lot of water. If you have a hard time shedding water weight, see your doctor to find out what’s causing the problem. They may be able to treat the underlying cause and give you medications to help you retain less water.Warning: Call your doctor immediately if you gain more than 2 pounds (0.91 kg) in a day or 4 pounds (1.8 kg) in a week. This can be a sign that you’re retaining too much water. Your doctor might recommend diuretic medications (water pills) or magnesium supplements to minimize how much water you retain. Common causes of fluid retention include allergic reactions, arthritis, kidney or liver problems, heart disease, and certain lung conditions. Some medications can also cause you to retain water.
Cutting Fat with Diet and Lifestyle Changes

Eat lean proteins to fill up faster. Eating plenty of protein forces your body to burn extra calories in the digestion process. It also fills you up longer than other types of foods, making you less likely to get hungry between meals. Try to eat 1 - 1.5 g of lean protein for every pound of body weight you’d like to weigh. Some healthy sources of lean protein include white meat poultry, fish, legumes (such as lentils, beans, and peas), and Greek yogurt.

Avoid liquid calories. It’s easy to pack in extra calories from the things you drink without even realizing it. If you’re trying to slim down quickly, avoid beverages that are high in calories and sugar, such as alcohol, sugary soda, juice, or sweetened coffees and teas. Stick to water to keep yourself hydrated. Not only will it help you shed water weight, but drinking plenty of water can also help you feel less hungry.

Stick to 3 light meals a day to encourage your body to burn calories. Instead of eating several small meals throughout the day, eat 3 light but filling meals daily while you’re trying to lose weight. Your meal should include a lean protein, fruits or vegetables, and a whole grain. Once you’ve eaten, resist the urge to snack until it’s time for your next meal. You’re more likely to lose weight if you eat fewer calories than you burn throughout the day.
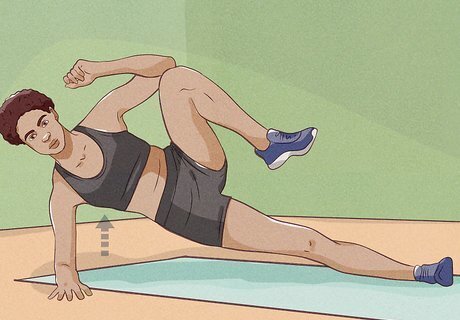
Boost your metabolism with high-intensity interval training. Doing high-intensity exercise can increase your metabolism and encourage your body to burn fat. Talk to your doctor, physical therapist, or personal trainer about trying high-intensity interval training to get your heart pumping and burn calories quickly.Tip: Strength training is also a great way to burn fat and help define your muscles. Don’t be discouraged if you don’t see the number on the scale going down, however—you may be putting on muscle mass! Try doing circuits of intense exercise for 30 seconds followed by 15 seconds of slower exercise. Some good exercises for a high-intensity workout include lunges, jump squats, and jumping jacks.

Ask your doctor about going on a low-calorie diet. If you need to lose fat in a hurry, a low-calorie diet is an option. These diets usually involve limiting yourself to a smaller amount of calories per day. Keep in mind, however, that this isn’t a good option for long-term weight loss. Try a low-calorie diet only under the supervision of a doctor or registered dietitian, and don’t keep it up any longer than they recommend. Eating a low-calorie diet may be dangerous if you’re pregnant, nursing, or have certain health conditions, such as a vitamin deficiency or eating disorder.



















Comments
0 comment