views
Basic Troubleshooting
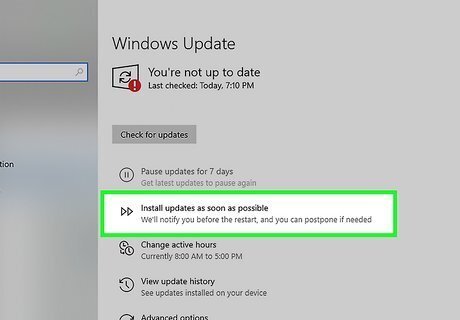
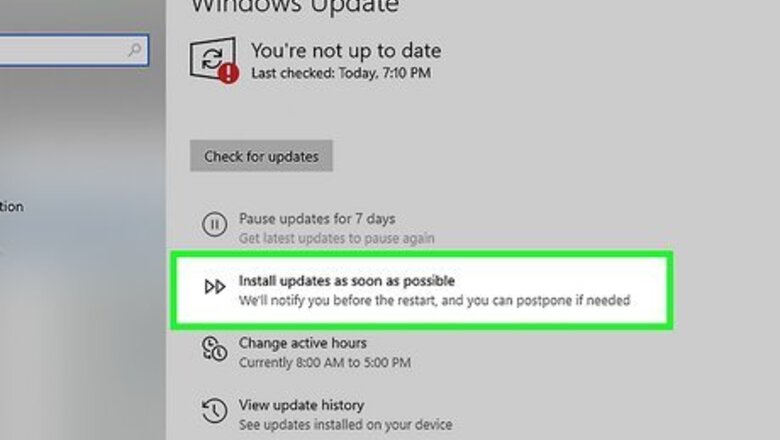
Install all Windows updates as well as the latest service packs. Windows updates can patch out security vulnerabilities and improve the performance of the system. Always be sure to keep Windows up-to-date.
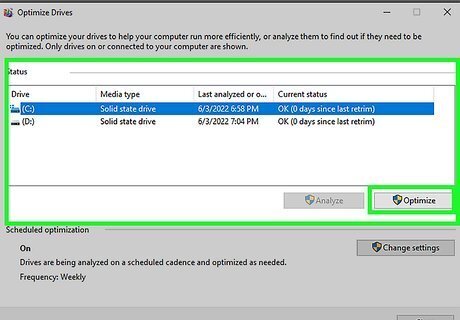
Defragment your hard disks. Over time, data on your hard drive gets scattered across various locations on your hard drive. This makes it harder for your computer to load the data it needs. Defragmenting your hard drive reorganizes your hard drive so that all the data is stored in a more organized manner. Use the following steps to defragment your hard drive: Select the search bar on the taskbar and type defrag. Click Defragment and Optimize Drives. Select the disk drive you want to optimize. Click Optimize. Click Optimize again.
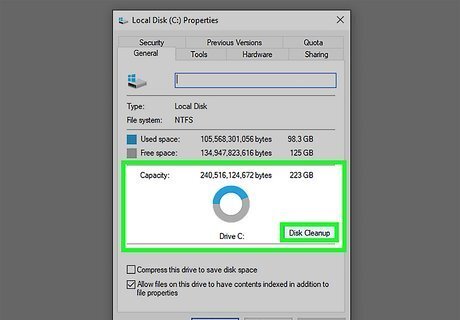
Run Disk Cleanup Utility. This removes temporary files and cache that your system uses and frees up some hard drive space. You can do so using File Explorer on Windows. Use the following steps to run Disk Cleanup Utility: Press Windows key + E to open File Explorer Click This PC, My Computer or something similar. Right-click the drive with your Windows installation ( it's usually the "C:" drive), Click on Properties. Click the button that says Disk Cleanup, located next to the graph demonstrating disk usage. Click the checkbox next to the files you want to delete. Click Ok. Click Delete Files.
Run an antivirus scan. Windows has it's own built-in Antivirus scanner you can use to scan for viruses, but you may want to use a third-party antivirus app, such as Malwarebytes or Avast Anti-Virus. If you have a persistent problem with viruses and malware, you may want to boot your PC into Safe Mode and run an antivirus scan.
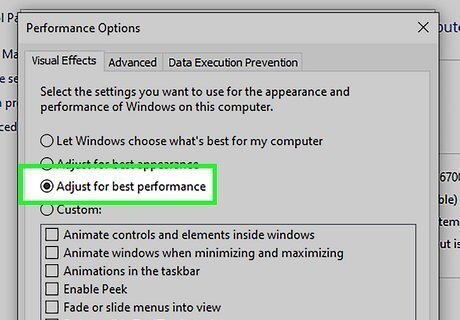
Set your Windows settings for "best performance." This will reduce the number of visual effects Windows uses and set your Windows settings for the best performance. Use the following steps to set your Windows settings to "Best Performance:" Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings/Gear icon. Click About. Click Advanced System Settings in the menu to the right. Click Settings under "Performance." Click the radio option next to "Adjust for best performance." Click Apply. Click Ok.
Downgrade your image quality. Downgrading your image quality gives your computer less detail to process and can improve your PC's performance. Use the following steps to downgrade your image quality: Right-click your computer's desktop. Click Display Settings. Use the drop-down menu below "Display resolution" to select a lower resolution.
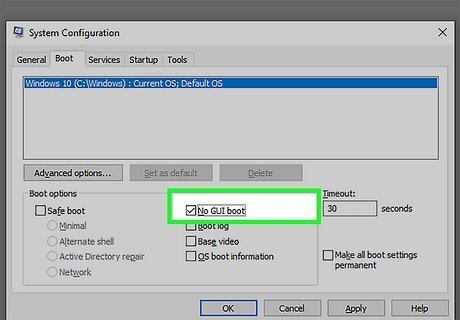
Change your boot settings. Windows allows you to select the option to boot your PC with minimal settings. This can improve your boot time. Use the following steps to change your boot mode: Press Windows key + R to open Run. Type msconfig next to "Open" and click Ok. Click the Boot tab. Click the checkbox next to "No GUI Boot." Alternatively, you can the checkbox next to "Safe Boot" and make sure "Minimal" is selected.
Removing Unwanted Programs and Files
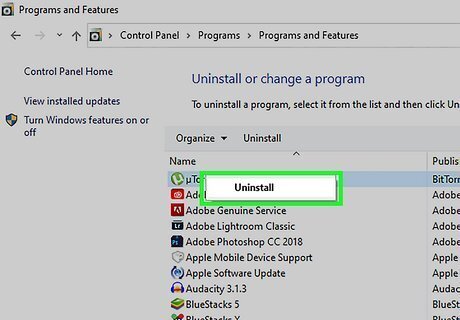
Remove unused software and programs. Sometimes programs run in the background, unseen by the user, but added together, it can take up quite a bit of computer resources. Use the following steps to uninstall programs from a Windows computer: Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings/Gear icon. Click Apps Click Programs and features in the upper-right corner. Click a program you want to uninstall. Click Uninstall above the list of apps. Follow the instructions to uninstall the app.
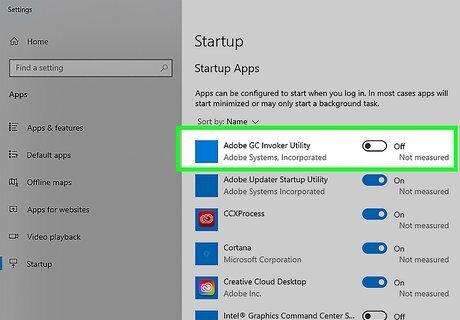
Remove startup services that you don't use. Startup services are programs that start up automatically when you boot up your PC. Having too many programs starting up at once during startup can slow down your boot process. Some programs may set themselves to start up without you knowing. Use the following steps to remove startup programs you don't use: Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings/Gear icon. Click Apps. Click Startup in the menu panel to the left. Click the toggle switch next to any startup apps you don't want to startup during the boot process.
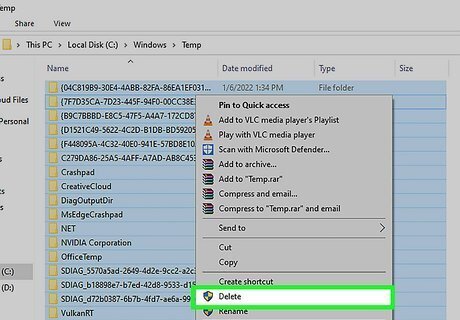
Clean out your Temp files. Windows temp files are temporary files Windows uses to quickly recall information. Clearing them can free up space and speed up your computer. To delete your temp files, you first need to open File Explorer and set it to display hidden files and folders. Then use the following steps to clear your Temp files: Press Windows key + R to open Run. Type %temp% next to "Open" and click Ok. Press Ctrl + A to select all files. Press the Delete key.
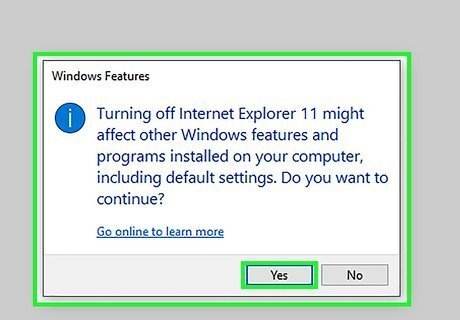
Remove unnecessary Windows components. Be sure to check the files that you want to install or keep, and uncheck those that you want to disable. Be very careful here, because you can disable some features that you may want to keep by accident. Use the following steps to disable Windows components: Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings/Gear icon. Click Apps Click Programs and features in the upper-right corner. Click Turn Windows Features on or off in the upper-left corner. Uncheck any Windows components you don't want to use.
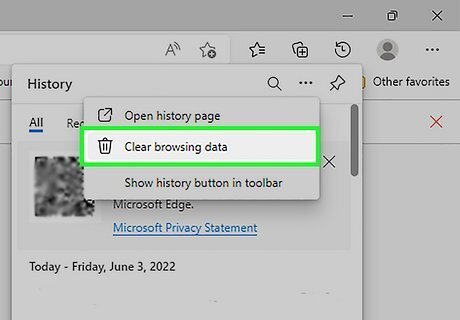
Remove your internet browsing history. The way you do this is different with each internet browser, but most have the option to delete your history in the options menu.
Clean your registry. You can find several free registry cleaners on the internet. These include CCleaner and Wise Registry Cleaner. You can also use a registry defragmenter to defrag your page file and registry as well.
Avoid desktop manipulation programs. These programs include Stardock or Fences. These programs can slow down your computer, especially if it has a low amount of RAM.
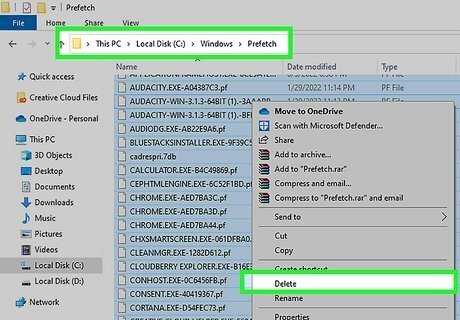
Clean out your Prefetch folder. The Prefetch folder contains files your Windows system uses to speed up the load time for your apps. Cleaning out these files gives Windows an opportunity to refresh these files. It's important that you do not delete the Prefetch folder itself. Use the following steps to clean out the Prefetch folder: Press Windows key + R to open Run. Type Prefetch next to "Open" and click Ok. Press Ctrl + A to select all files in the Prefetch folder. Press the Delete key.
Hardware Solutions
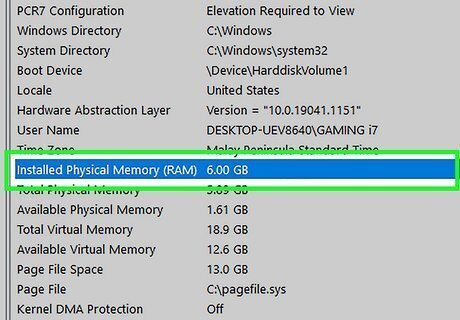
Try adding more RAM. Windows 10 requires at least 4 GB of RAM in order to run properly. Most modern computers have at least 8 GB of RAM.
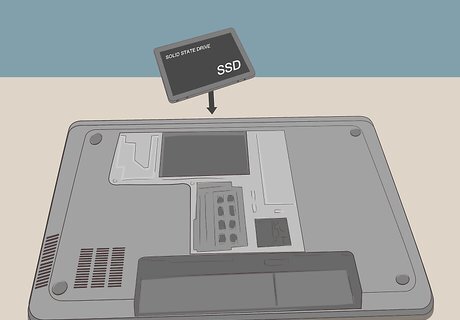
Consider switching to an SSD. SSD stands for Solid State Drive. These are newer hard drives that have no moving parts. They are much faster than older hard drives, known as Hard Disk Drives (HDD). You can backup your current hard drive and install a new SSD. Then you will need to install Windows again before restoring your backup files to the SSD.
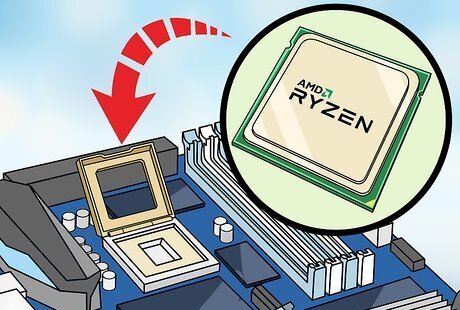
Consider upgrading your processor. If your computer is unable to run modern software, you may want to consider upgrading your computer processor. Before you purchase a new computer processor, you'll need to know what type of motherboard your computer has. You'll then need to check to make sure the new processor is compatible with your motherboard. If you know to fix computers, you can replace the computer processor check yourself. You can also have it installed by a professional technician. If the processor you want is not compatible with your motherboard, you may want to consider replacing your entire motherboard.

Consider upgrading your graphics card. Your graphics card is responsible for rendering images and graphics. Most modern graphics card have their own built-in graphics processor called a GPU. In addition to improving your computer's graphics rendering abilities, in some cases, the GPU can be used to supplement your computer's processor and reduce it's workload.
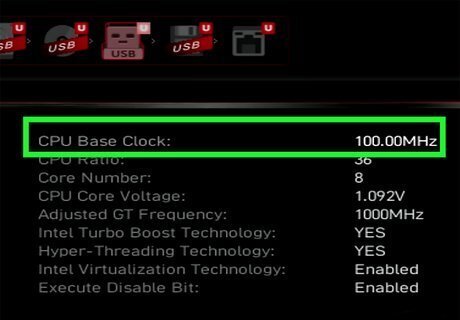
Consider overclocking your computer. Overclocking is when you set your computer's clock speed to run faster than the manufacturer's default setting. This makes your computer run faster. You can overclock your processor as well as your graphics card. Warning: Overclocking your computer can cause your processor or graphics card to overheat and do damage to your computer. Do not overclock your computer unless you know what you are doing and are willing to assume the risk.
Replacing Your Operating System
Reinstall your operating system. This should only be used as a last resort. If you've tried everything and your computer is still unbearably slow, you may need to reinstall your operating system. Warning: Reinstalling your operating system will most likely erase all the data on your hard drive. Be sure to back up all files and data you want to keep before attempting to reinstall your operating system.
Consider switching to Linux. If you are using an older computer, it's possible that it may not have the hardware to properly run newer operating systems. Switching to Linux may be a good way to prolong the life span of your computer. Linux is a much more efficient operating system than Windows or macOS. Warning: Before switching to Linux, consider that many popular apps and software do not work for Linux. Programs like Microsoft Office, Adobe Creative Cloud, and many popular games do not have a Linux version. However, you may be able to find free alternatives to these programs for Linux. For example, instead of using Microsoft Office, you may be able to use LIbre Office instead.
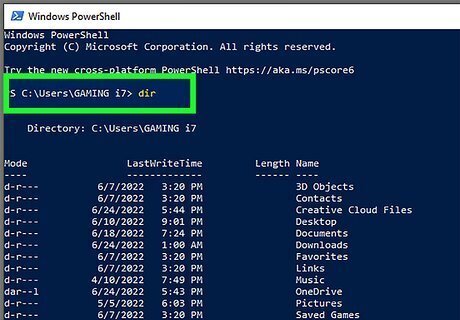
Consider using the command-line. Command Line Interfaces (CLI) is a text-based interface where you use text commands instead of graphical user interface (GUI). If requires a little more know-how, but you can still run most of the programs you use using a CLI. Linux OS and BSD makes it easier to use the command-line, whereas Mac OS X and Windows, not so much. The following are some commands you can use with a command-line interface: action Windows/DOS Windows Powershell,Mac OS X, Linux, BSD etc. list directory dir ls clear console cls clear copy file(s) copy cp move file(s) move mv delete file(s) del rm create directory md mkdir remove directory rd rm -rf change current directory cd cd current directory cd, chdir pwd search find grep concatenate cat cat permissions chmod chmod display/output text echo echo add user net user adduser




















Comments
0 comment