
views
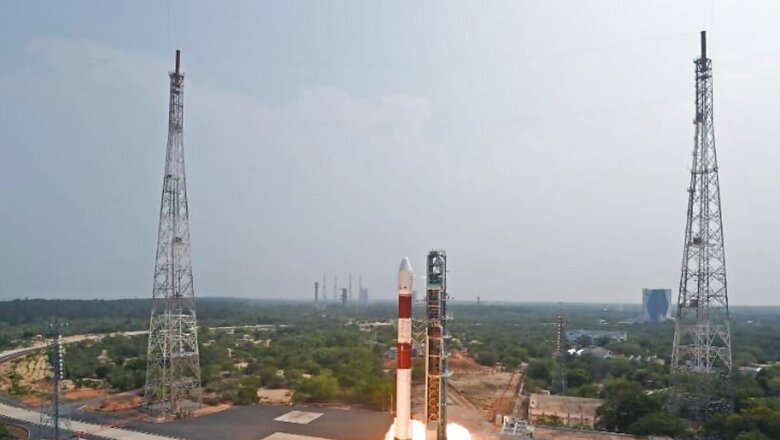
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Saturday conducted an “in-orbit scientific experiment” using the fourth stage of a Polar satellite launch vehicle rocket.
Soon after ISRO’s PSLV C55 rocket successfully placed two Singapore satellites– TeLEOS-2 and Lumelite-4 into orbits after a 2.19 pm liftoff, the scientists used PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-2 (POEM-2) as an orbital platform to carry out the scientific experiments through non-separating payloads carried by it.
While the POEM is being written,here are initial ????… pic.twitter.com/cfoxt7Op8I— ISRO (@isro) April 22, 2023
Announcing the success of the satellite mission, ISRO Chairman S Somanath said “POEM is going to write some more poems” with seven payloads.
PSLV roaring into the sky ???? pic.twitter.com/baSVrpoR7M— ISRO (@isro) April 22, 2023
The payloads belong to ISRO, Bellatrix, Dhruva Space and Indian Institute of Astrophysics.
#WATCH | “We are very happy that it did very well. We want private people of India should come in space… This will create more jobs, industries and business…,” says ISRO chief S Somanath on launch of PSLV-C55 with two Singaporean satellites for Earth observation pic.twitter.com/h82pXxYccx— ANI (@ANI) April 22, 2023
It has a “deployable solar panel for the first time in the upper stage of a rocket.” “That is another exciting thing to happen,” Somanath added.
The payloads on POEM-2 would be powered by scientists to perform the operation. The platform’s solar panel would be deployed facing towards the Sun through a ground command.
The platform would ensure the deployed solar panel points towards the Sun optimally using appropriate sun pointing mode, which would increase the power generation capability.
The power would be provided to payloads and avionic packages based on their requirements.
Saturday’s campaign by the scientists is the third time that the fourth stage has been used after satellite separations as a platform for experiments.
(With PTI inputs)
Read all the Latest India News here

















Comments
0 comment