views
- Use "sudo hostnamectl set-hostname <newhostname>" to change the hostname on Linux.
- If you use GNOME, you can also set a hostname in Settings > About > Device name.
- To view your current hostname, use the command "hostnamectl" or "hostname."
- For a temporary hostname change, use "sudo hostname <newhostname>."
The Hostnamectl Command
Open a Terminal. If you're changing the hostname of a Linux server that you're signing in to remotely, log in now. If you're changing the hostname of your Linux desktop operating system, press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a Terminal. This method will work on any version of Linux that uses systemd, which is the majority of Linux distributions. This includes Ubuntu, Debian, Redhat, CentOS, OpenSUSE, Fedora, and Arch Linux.
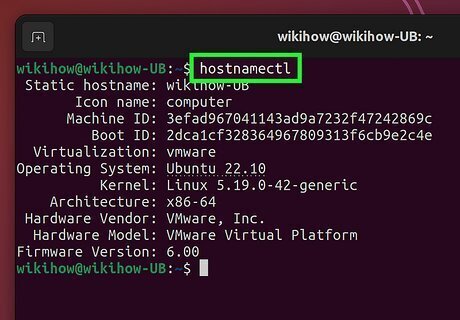
Run the hostnamectl command to view your current hostname. This displays your current hostname, along with your system architecture, kernel version, and other info. You can also run the command hostname to view your current hostname without any additional info.
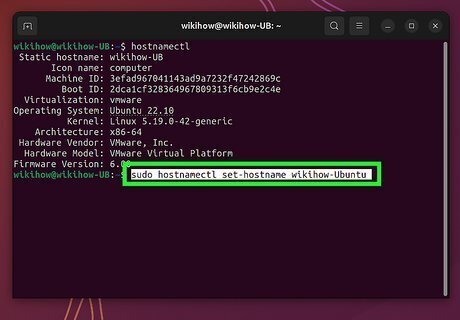
Run the command sudo hostnamectl set-hostname newhostname. Replace newhostname with the hostname you'd like to set. Once you run the command, your Linux hostname will be changed immediately. This command changes the static (standard), transient (dynamic), and pretty (descriptive) hostnames all at once. If you only want to change one type of hostname, you can use the --static, --transient, and --pretty options. Static and transient hostnames can contain letters, numbers, and hyphens only. Run the hostname command to see your new hostname. If the hostname hasn't changed run the command sudo systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed to restart systemd-hostnamed.
Network Manager CLI
Open a Terminal. If you're changing the hostname of a Linux server that you're signing in to remotely, log in now. If you're changing the hostname of your Linux desktop operating system, press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a Terminal. This method will show you how to use the Network Manager Command Line Interface (nmcli) to change the hostname on Linux. Nmcui comes with some distributions, including RedHat and CentOS. You can install Network Manager on Ubuntu and other Debian-based Linux systems using the command sudo apt install network-manager.
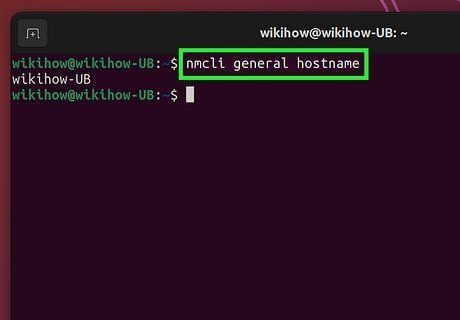
Run the command nmcli general hostname. This displays your Linux system's current hostname.
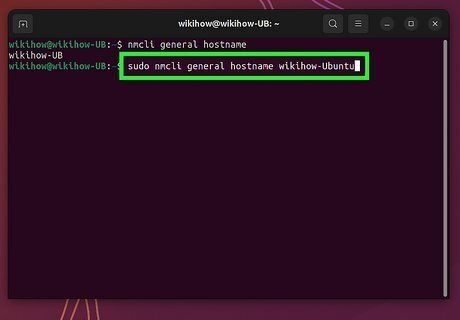
Run the command sudo nmcli general hostname newhostname. Replace newhostname with the hostname you'd like to set, using only letters, numbers, and hyphens. Your new hostname will be set instantly—no reboot required. To verify, run the command hostname. If your hostname has not changed, run the command sudo systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed to restart systemd-hostnamed.
Network Manager TUI
Open a Terminal. If you're changing the hostname of a Linux server that you're signing in to remotely, log in now. If you're changing the hostname of your desktop computer, press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a Terminal.
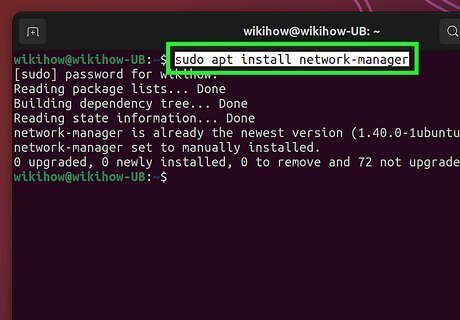
Install Network Manager TUI. In this method, we'll use the Network Manager Text User Interface (nmtui) to change the hostname. This tool is a graphical version of nmcli, but it isn't preinstalled on most distributions. To install on Debian-based systems, use sudo apt install network-manager. On Redhat and other RH-based Linux distros, use sudo dnf install NetworkManager-tui.
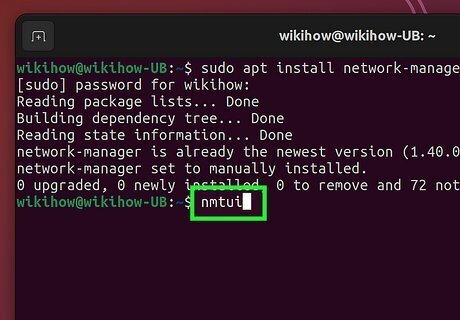
Run the command nmtui. This launches the graphical Network Manager tool.
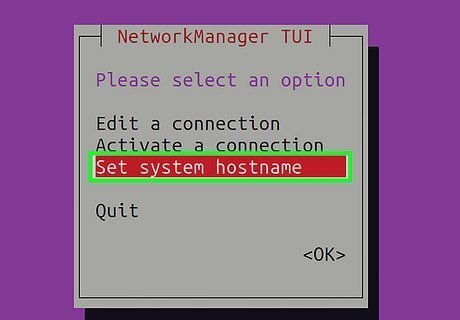
Select Set system hostname. You can navigate by pressing the Tab or arrow keys, and make selections using Enter. Once selected, your current hostname will appear.
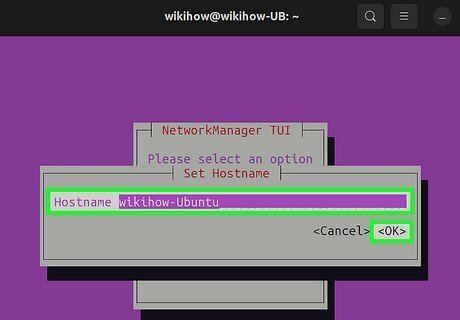
Enter your new hostname and select OK. You have now changed the hostname of your Linux system. You can verify your new hostname by running the hostname command at the prompt. If your hostname is not changed, run the command sudo systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed to restart systemd-hostnamed.
GNOME Settings
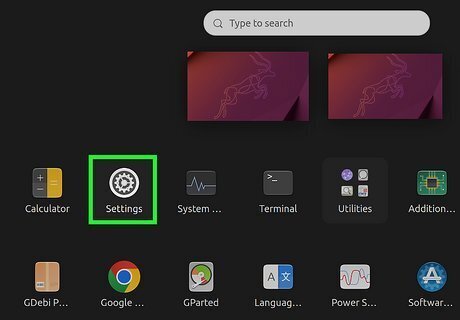
Open your GNOME settings. If you're using the GNOME desktop environment on Ubuntu, Fedora, or any other version of Linux, you can change the hostname in your settings.
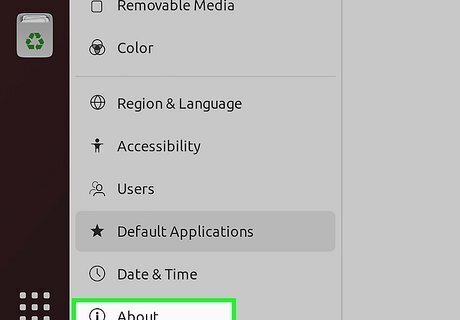
Click About. It's on the left panel. You'll see your current hostname next to "Device Name."
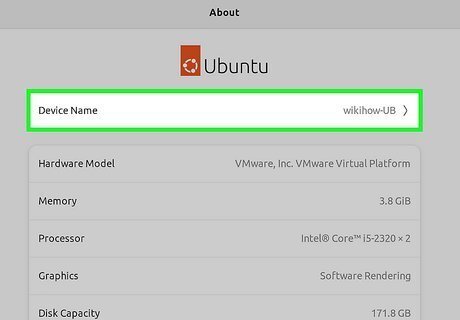
Click Device Name. Now you'll be able to replace your old hostname with a new one. Hostnames can contain the same characters as domain names—letters, numbers, and hyphens. If you enter a hostname that has spaces and special characters (e.g., "My Linux Laptop" instead of linux-laptop), you'll see that you've set the "pretty name," and that a new hostname is automatically assigned based on that name (e.g., "my-linux-laptop"). If you want to use one static hostname for everything, make sure to stick to the typical hostname/domain name conventions.
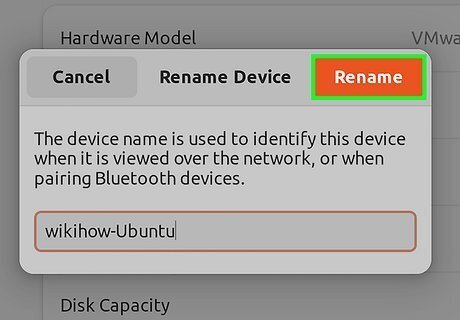
Enter a new hostname and click Rename. Your Linux hostname will update instantly.
The Hostname Command
Open a Terminal. If you're changing the hostname of a server that you're signing in to remotely, log in now. If you're changing the hostname of your Linux desktop operating system, press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a Terminal. You can use this method to temporarily change your hostname or make the change permanent.
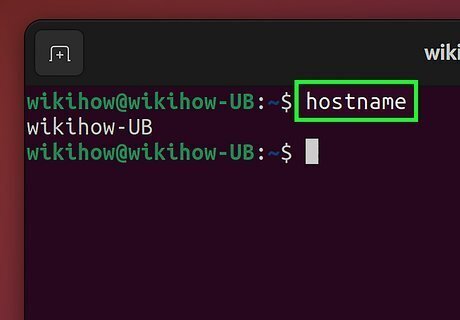
Use the hostname command to view the current hostname. While you'll also be using this command to change the hostname, running it without any options simply displays the current hostname.
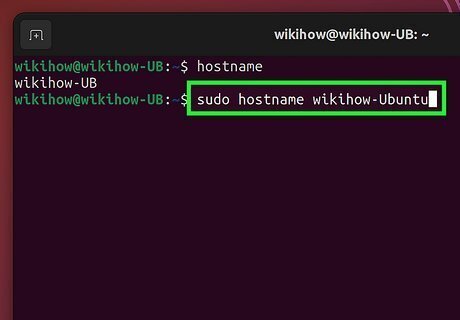
Run the command sudo hostname newhostname. Replace newhostname with the name you want to give your Linux system. Hostnames can include letters, numbers, and dashes (hyphens). As of now, your hostname is only changed temporarily. If you were to reboot now, the old hostname would return. If you want to change your Linux hostname permanently without rebooting, continue with this method.
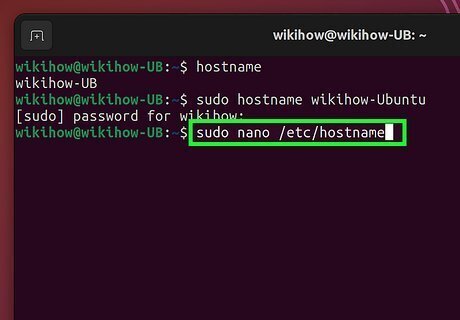
Update the hostname in /etc/hostname. The first step of making your hostname change permanent is to replace your old hostname in /etc/hostname with the new hostname. To open the file, run sudo nano /etc/hostname. Replace the old hostname with the new one. Press Ctrl + X, press Y for Yes, and then press Enter to save and exit.
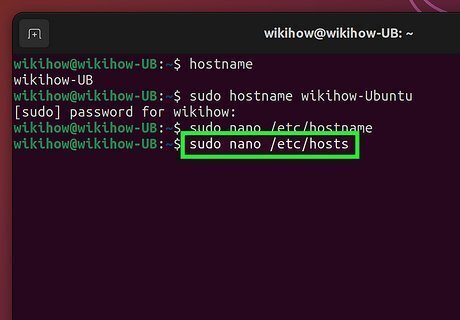
Update the hostname in /etc/hosts. The last step is to replace the old hostname with the new one in /etc/hosts: To open the file, run sudo nano /etc/hosts. Scroll down and replace your old hostname (the one next to 127.0.1.1 that is not localhost) with the new one. Press Ctrl + X, press Y for Yes, and then press Enter to save and exit. Your Linux hostname change is now permanent.















Comments
0 comment