
views
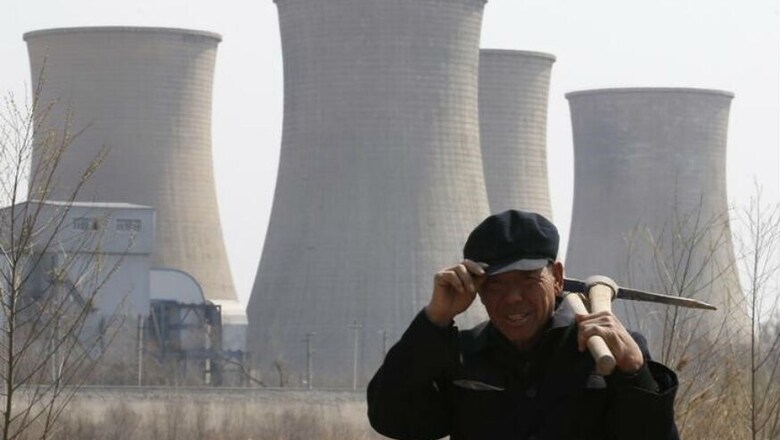
Brussels: The European Union introduced new rules on Wednesday to guard against excessively cheap imports and singled out China for special attention in a report spelling out how its economy is distorted by the state.
In a 465-page report, the European Commission concluded that Beijing exerts a decisive influence over the allocation of resources, such as land or capital, and influences prices of various factors of production "in a very significant manner".
The report is significant because the EU has changed the way it handles anti-dumping cases.
After two years of debate on the subject, the EU has agreed that dumping means selling for export at below domestic prices for all World Trade Organization (WTO) members, of which China is one.
However, it will take a different approach for cases of "significant market distortions", an exception expected to cover many Chinese firms, some already subject to import duties.
In such cases, it will use international benchmarks to calculate a fair price for a product.
The European Commission, which oversees trade policy in the 28-member EU, said reports it produces on industries or sectors are designed to guide EU producers who want to lodge complaints.
At the launch of the new rules on Wednesday, it had produced just one report - on China. However, it also said Russia could be next.
China last year launched a complaint at the WTO against Europe and the United States over their trade defence practices.. It has also demanded that they recognise its right to be considered a normal "market economy" at the end of 2016, some 15 years after it joined the WTO.
However, the Commission report released on Wednesday said China's "socialist market economy" was something different.
It said the Chinese Communist Party sets and controls all aspects of the economic agenda, with banks as instruments to carry it out in a "rigid and distorted" financial system and preferential treatment of domestic companies enshrined.
Chinese businesses in targeted sectors receive land at very low prices or even for free, cheap energy, preferential access to capital, artificially low borrowing costs, with highly controlled raw material prices and limited workers' rights.
Separate sections in the report on the steel, aluminium, chemicals and ceramic sectors detail state intervention, leading to overcapacity.
While China may have committed to curtailing overcapacity, the report says its industrial policy had led to the opposite, often with state-owned companies leading the charge.
The word "distortion" and "intervention" feature respectively 92 and 95 times in the report.



















Comments
0 comment